Understanding the Scientific Method for School Projects
Whether you’re preparing a science fair project, writing a lab report, or exploring how something works, the scientific method is the foundation of all scientific investigation. It helps students think logically, test ideas, observe results, and make conclusions based on evidence rather than guesses. Many students organize their experiment worksheets, observation charts, and lab notes into PDF study packets using PDFmigo.com.
What Is the Scientific Method?
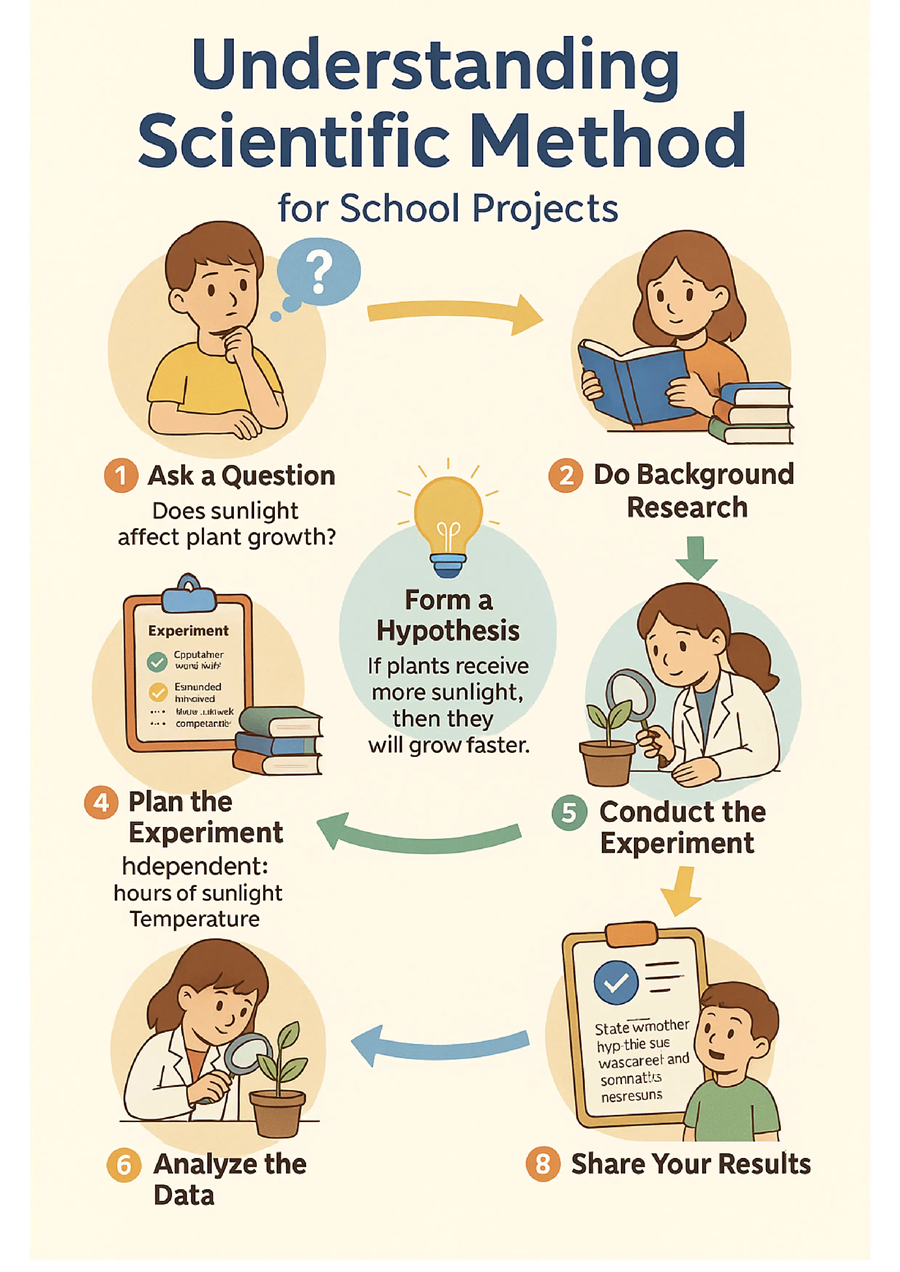
The scientific method is a step-by-step process that scientists use to ask questions, test ideas, and discover answers. Students use it in chemistry labs, biology activities, physics experiments, and even at-home science fair projects.
Step 1: Ask a Question
Every experiment begins with a clear, testable question. A good scientific question starts with:
- How does…?
- What happens if…?
- Does ___ affect ___?
Example: “Does sunlight affect how fast plants grow?”
Step 2: Do Background Research
Before making predictions or designing the experiment, learn what scientists already know about your topic. You might search online, read textbooks, or watch educational videos.
Taking clear notes and saving your research in PDFs makes the project easier to organize. Many learners combine these files using Merge PDF.
Step 3: Form a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is an educated guess—a possible explanation or prediction based on your research.
Example: “If plants receive more sunlight, then they will grow faster.”
Step 4: Plan the Experiment
Your experiment must be structured so other students could repeat it. Planning includes:
- Variables: the conditions you change or measure
- Materials: the tools and supplies you need
- Procedure: step-by-step instructions
- Controls: things you keep the same in every trial
Example variables:
- Independent variable: hours of sunlight
- Dependent variable: plant growth
- Controlled variables: soil type, water amount, temperature
Step 5: Conduct the Experiment
Follow your procedure carefully and record everything you observe. Accurate data is essential for reliable results.
Keep track of:
- Measurements
- Times and dates
- Changes in appearance
- Unexpected problems
Step 6: Analyze the Data
Once the experiment is complete, review your results. Look for patterns:
- Did the dependent variable change?
- Did the results match your hypothesis?
- Were there any outliers or errors?
Creating charts and graphs helps you see the data clearly. Many students export graphs and tables as PDFs and include them in their final project report.
Step 7: Draw a Conclusion
A conclusion answers the original question and states whether your hypothesis was correct.
Your conclusion should explain:
- What you discovered
- Why the results happened
- Possible errors or improvements
- What you would test next time
Step 8: Share Your Results
In school projects, you may share your results in a report, slideshow, or display board. This is your chance to communicate your findings to others.
Most students create digital reports by combining their background research, hypothesis, experiment notes, and final data charts into one file using tools at PDFmigo.com.
Why the Scientific Method Matters
The scientific method teaches students:
- How to think logically
- How to solve real-world problems
- How to understand cause and effect
- How to analyze evidence instead of guessing
These skills are useful not only in science class, but in everyday life—making decisions, solving problems, and evaluating information.
Final Thoughts
The scientific method is powerful because it turns curiosity into knowledge. By asking good questions, making predictions, testing ideas, analyzing results, and drawing conclusions, students learn to explore the world like real scientists. With organized notes, careful observations, and clear reporting, any student can create a strong science project using this method.





